

MHRA 'DNA', All Acronyms, 22 July 2023, Bluebook All Acronyms, DNA (Jul. The letters DNA stand for Deoxyribonucleic acid, and this essentially refers to the shape and content of the molecule, however, the full name is quite a mouthful so it’s shortened to DNA for clarity and ease of use.

DNA, All Acronyms, viewed July 22, 2023, MLA All Acronyms. Retrieved July 22, 2023, from Chicago All Acronyms. It is the genetic information that every parent passes on to their biological children. Your browser does not support the audio element.Facebook Twitter Linkedin Quote Copy APA All Acronyms.

Dna stands for... code#
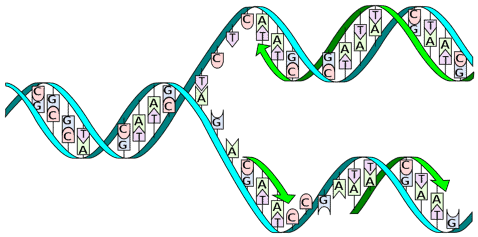
Oswald Avery in 1944, for example, proved that the genetic code that DNA was indeed the carrier of hereditary information, ending more than 80 years of productive speculation. It's that 0.1 percent that is different that makes us all unique. The story of the genetic code is the story of biology and genetics in the 19th, 20th, and 21st centuries, as well as its promises and its perils. About 99.9 percent of the DNA of every person on the planet is exactly the same.You can think of them like puzzle pieces: A only connects with T and G only connects with C. Only certain sets of nucleotides can fit together. Every living creature has its own unique DNA and no one except for an identical twin will have the same DNA as you. Deoxyribonucleic acid is the genetic code of a living thing. The other acid is ribonucleic acid (RNA). Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is the main acid.
Dna stands for... free#
The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of all known organisms and many viruses. DNA - What does DNA stand for The Free Dictionary TheFreeDictionary DNA Also found in: Dictionary, Thesaurus, Medical, Legal, Idioms, Encyclopedia, Wikipedia. There are two different nucleic acids that make up the different strands of DNA. A different nucleotide connects to each backbone and then connects to another nucleotide in the center. Deoxyribonucleic acid is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. Between the backbones are the nucleotides represented by the letters A, T, C, and G. There are two sets of backbones that twist together. On the outside of the double helix is the backbone which holds the DNA together. Proteins are used by the cell to perform certain functions, to grow, and to survive.Īlthough DNA looks like very thin long strings under a microscope, it turns out that DNA has a specific shape. The conformation that DNA adopts depends on the hydration level, DNA sequence, the amount and direction of supercoiling, chemical modifications of the bases, the type and. DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the hereditary material that lies within the nucleus of all cells in humans and other living organisms.
Dna stands for... how to#
A gene tells a cell how to make a specific protein. DNA exists in many possible conformations that include A-DNA, B-DNA, and Z-DNA forms, although only B-DNA and Z-DNA have been directly observed in functional organisms. Within each string of DNA are sets of instructions called genes. This allows for billions and billions of different combinations. This resource was developed to support the comprehensive, evidence-based, peer-reviewed PDQ cancer genetics information summaries. Even though there are only four different letters, DNA molecules are thousands of letters long. A dictionary of more than 150 genetics-related terms written for healthcare professionals.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
